Branching workflows
Main branches
- Master. Master branch contains the latest “release” code (code of the latest production version of the product)
- Maintenance. Maintenance branch contains the latest “release” code. Maintenance branch should be created in case, when bug found in latest release.
- Staging. Staging branch contains the code of “release candidate” (next release version).
- Development. Development branch contains “ready for testing” code of the product.
!!! Danger "Main branches should be protected!"
Work branches
- Feature branch name should be: feature/FeatureId_FeatureName. Where FeatureId - Redmine feature id, FeatureName - name of the feature. For example: for feature with name “Sign in” feature branch name should be feature/123_signin.
- Task branch name should be: task/TaskId_TaskName. Where TaskId - Redmine task id, TaskName - name of task. For example: for task with name “Data model” task branch name should be task/321_data_model.
- Bug branch name should be: bug/BugId_BugName. Where BugId - Redmine bug id, BugName - name of bug. For example: for bug with name “Incorrect error message” bug branch name should be bug/231_incorrect_error_message.
!!! tip "PS. Branches should have clear names." - Example with incorrect name: task/bugfix. - Bug branch name should start from “bug”, not from “task” or something else. - Bug branch name should have clear name, not “bugfix”. Fix for which bug that branch contains?
Relation: branch to environment
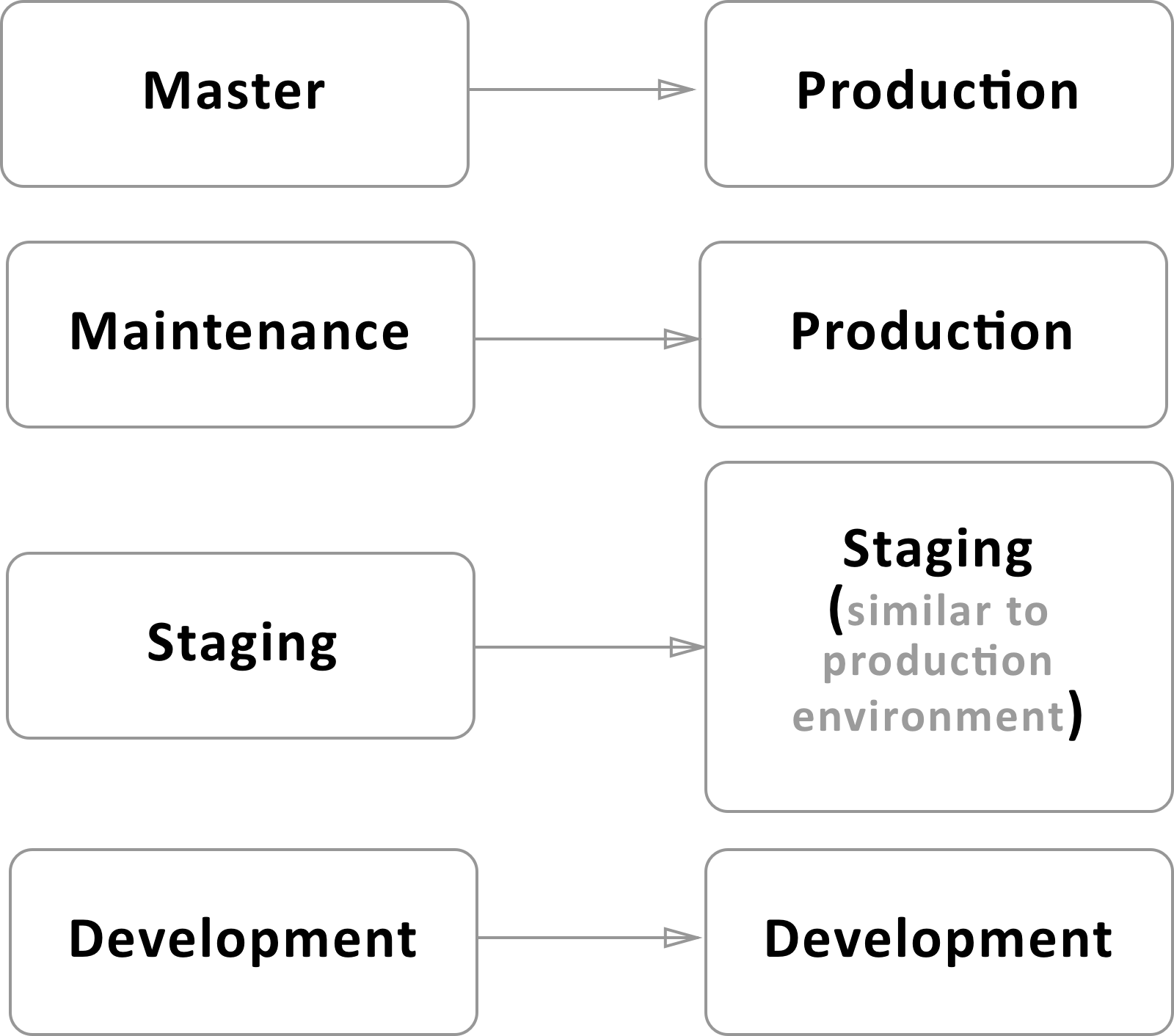
Branching strategy
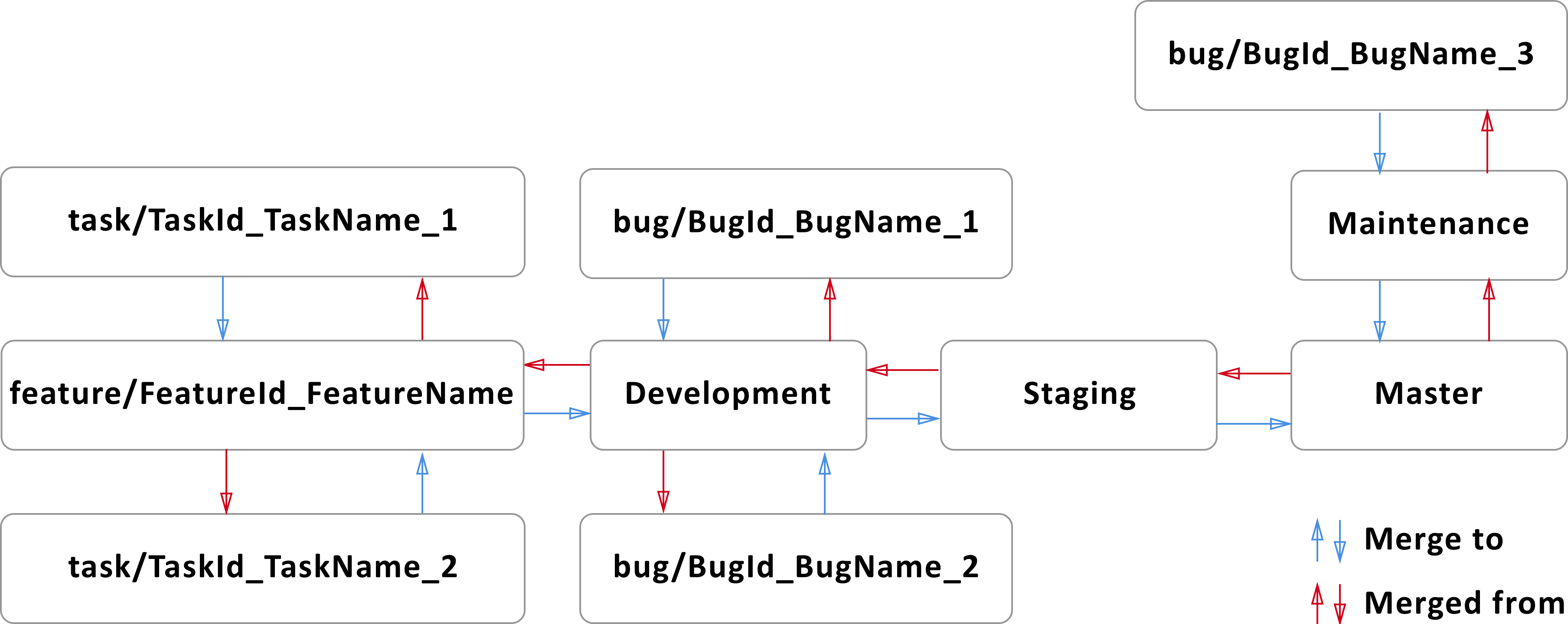
Hierarchy
- Master branch hasn’t “parent” branch. Master - it’s a main branch.
- Maintenance branch should be branched from Master branch.
- Staging branch should be branched from Master branch.
- Development branch should be branched from Staging branch.
- Feature branch (feature/FeatureId_FeatureName) should be branched from Development branch.
- Task branch (task/TaskId_TaskName_1, task/TaskId_TaskName_2) should be branched from Feature branch (feature/FeatureId_FeatureName).
- Bug branch (bug/BugId_BugName_1, bug/BugId_BugName_2) should be branched from where it was found (for example Development branch).
- Bug branch (bug/BugId_BugName_1, bug/BugId_BugName_3) should be branched from where it was found (for example Maintenance branch).
Workflow (Task)
- Task branch should be branched from Feature branch.
- After local changes all actual changes should be commited.
- Task branch should be merged with Feature branch (many developers can work with this task).
- Task branch should be pulled (in cases, when that branch already exist in origin).
- Task branch should be pushed to remote repository.
- When work with Task branch was finished, branch can be merged to Feature branch (Developer should create merge request at GitLab web interface).
Workflow (Main branches)
!!! tip "Precondition:" - Child branch = Development branch for example. - Parent branch = Staging branch for example.
- After local changes all actual changes should be commited.
- Child branch should be merged with Parent branch.
- Child branch should be pulled (in cases, when that branch already exist in origin).
- Child branch should be pushed to remote repository.
- When work with Feature branch was finished, branch can be merged to Development branch (Developer should create merge request at GitLab web interface).
Branching strategy (Bug fixing)
Case 1 (Bug was found in Master branch)
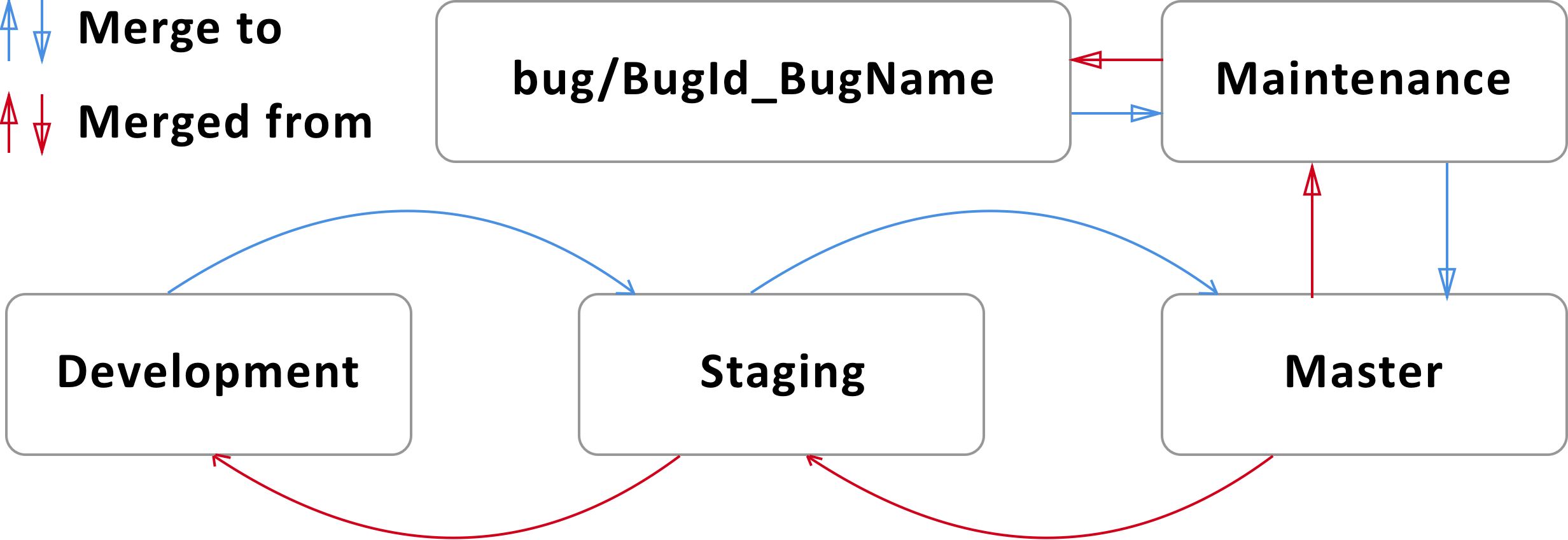
- Maintenance branch should be branched from Master branch.
- Bug branch (bug/BugId_BugName) should be branched from Maintenance branch.
- After local changes all actual changes in Bug (bug/BugId_BugName) branch should be commited.
- Bug branch should be merged with Maintenance branch.
- Bug branch should be pulled (in cases, when that branch already exist in origin).
- Bug branch should be pushed to remote repository.
- Maintenance branch should be merged with Master branch.
- Maintenance branch should be pulled.
- Maintenance branch should be pushed to remote repository.
- When work with Maintenance branch was finished, branch can be merged to Master branch (Developer should create merge request at GitLab web interface).
- After merging to Master branch changings should be merged to Staging and then to Development branch.
Case 2 (Bug was found in Staging branch)
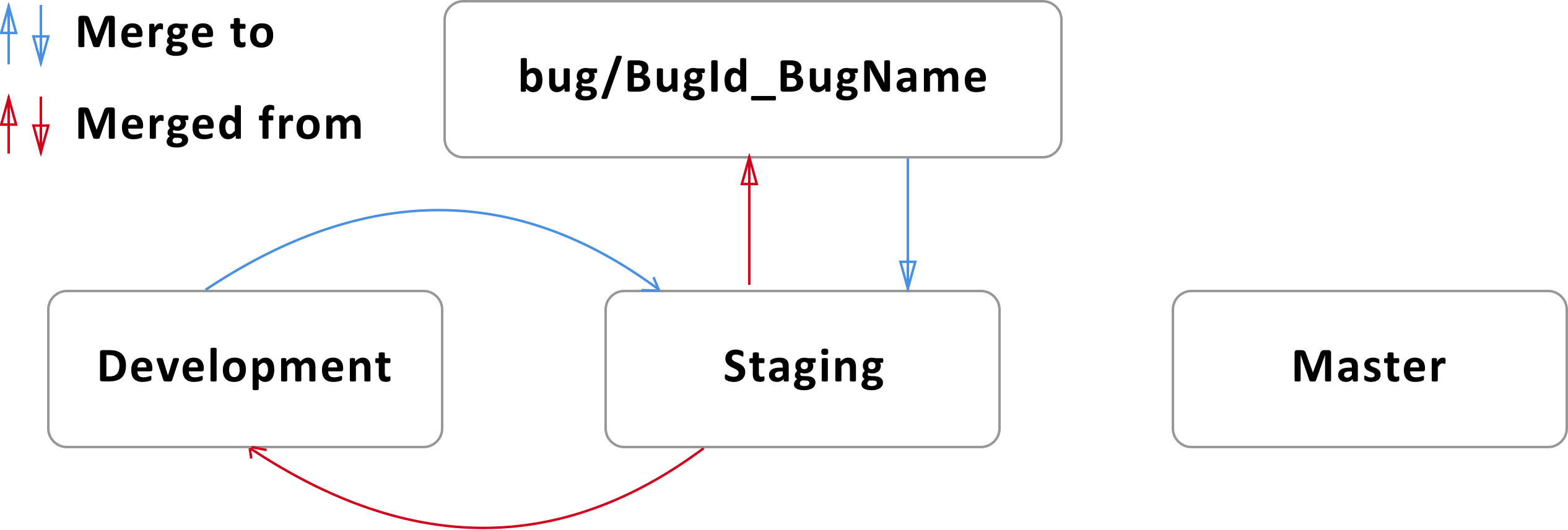
- Bug branch (bug/BugId_BugName) should be branched from Staging branch.
- After local changes all actual changes in Bug branch should be commited.
- Bug branch should be merged with Staging branch.
- Bug branch should be pulled (in cases, when that branch already exist in origin).
- Bug branch should be pushed to remote repository.
- When work with Bug branch was finished, branch can be merged to Staging branch (Developer should create merge request at GitLab web interface).
- After merging to Staging branch changings should be merged to Development branch.
Case 3 (Bug was found in Development branch)
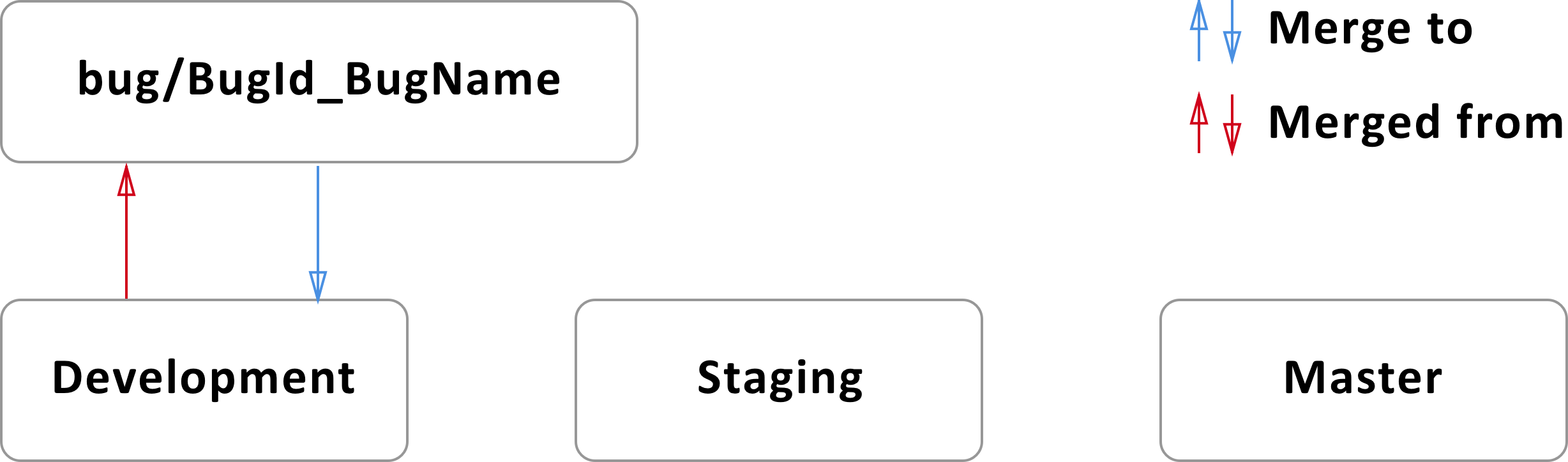
- Bug branch (bug/BugId_BugName) should be branched from Development branch.
- After local changes all actual changes in Bug branch should be commited.
- Bug branch should be merged with Development branch.
- Bug branch should be pulled (in cases, when that branch already exist in origin)
- Bug branch should be pushed to remote repository.
- When work with Bug branch was finished, branch can be merged to Development branch (Developer should create merge request at GitLab web interface).
